The Foundation of the Modern Data Center: Understanding Server Virtualization
In the world of information technology, one of the most transformative and foundational technologies of the past two decades has been Server Virtualization. At its core, this is the process of using a software layer, known as a hypervisor, to partition a single physical server into multiple, isolated virtual machines (VMs). Each VM can run its own independent operating system and applications, all while sharing the resources of the underlying physical hardware. This innovation breaks the traditional "one server, one application" model, which was incredibly inefficient, leading to massive server sprawl and underutilization. By enabling multiple applications to run safely and efficiently on a single piece of hardware, server virtualization dramatically increases server utilization, reduces costs, and provides a new level of flexibility and agility for IT operations, forming the bedrock of the modern, software-defined data center.
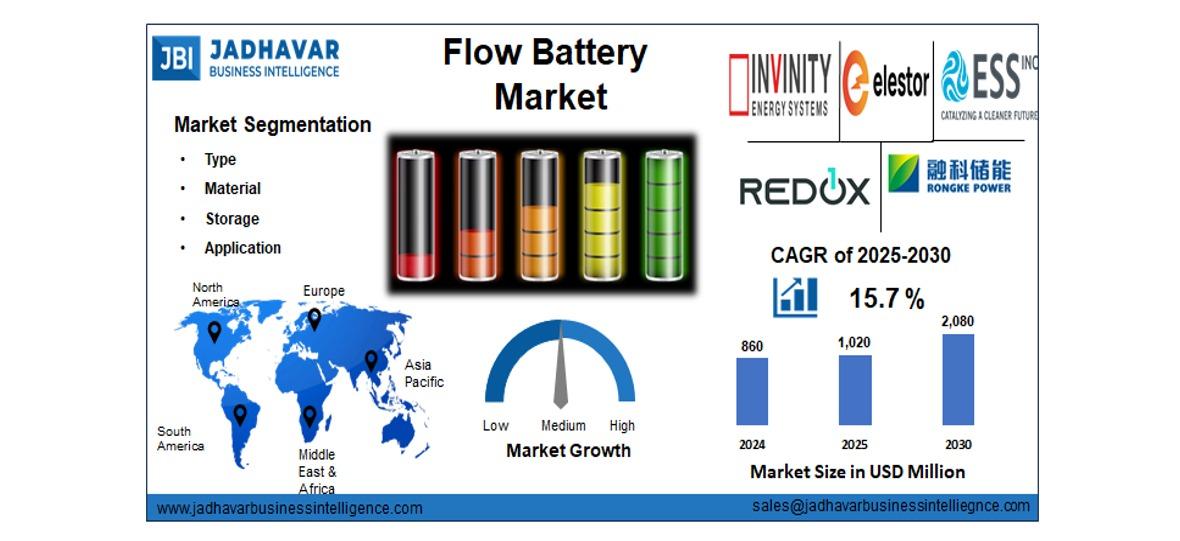
This fundamental re-architecting of the data center is the driving force behind a massive and consistently growing global market. The server virtualization industry is on a path of steady and sustained expansion, with its market size projected to grow to an impressive USD 16,093.62 million by the year 2035. This substantial growth will be powered by a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% during the 2025-2035 forecast period. This financial momentum is a direct reflection of the indispensable role that virtualization plays in modern IT. As businesses continue to seek greater efficiency, resilience, and agility from their IT infrastructure, the investment in virtualization technology and the expertise to manage it remains a critical and ongoing priority, driving this robust and long-term market expansion.
The benefits of server virtualization are profound and have fundamentally changed the economics of IT. The most significant advantage is a massive increase in hardware utilization and a corresponding reduction in the number of physical servers required. This leads to dramatic savings in hardware costs, as well as significant reductions in the power, cooling, and physical space needed for the data center, a major benefit for both the bottom line and the environment. Virtualization also provides a new level of operational flexibility. VMs can be easily created, moved, and copied, which dramatically speeds up the process of provisioning new applications and enables powerful disaster recovery capabilities. This ability to treat infrastructure as a flexible, software-defined resource is the core of its transformative power.
Looking ahead, while the initial wave of server virtualization has largely been completed in many enterprises, the technology continues to evolve and remains critically important. The rise of containerization, with technologies like Docker and Kubernetes, is often seen as the next step in the evolution of virtualization, offering a more lightweight and efficient way to package and run applications. However, these two technologies are not mutually exclusive; in fact, the vast majority of containerized applications today are run on top of virtual machines. The future of server virtualization lies in its role as the stable and secure foundational layer for a multi-faceted IT environment that includes both traditional applications in VMs and modern, cloud-native applications in containers, ensuring its continued relevance for years to come.
Explore Our Latest Trending Reports:
Japan Mesh App Service Architecture Market