Electric Bus Charging Systems Powering the Future of Sustainable Public Transport
The global transition to cleaner mobility has accelerated the adoption of electric bus charging systems, a crucial component driving the expansion of zero-emission public transportation networks. As cities strive to reduce pollution and improve urban air quality, electric buses have become a preferred solution — but their success relies heavily on efficient, scalable, and smart charging infrastructure. To explore market trends and growth opportunities, visit the Automotive Electric Bus Market Report.
The Growing Role of Electric Bus Charging Systems
Electric buses represent a vital step toward achieving sustainable transportation goals. Unlike traditional diesel-powered fleets, they operate quietly and emit no tailpipe pollution, making them ideal for densely populated cities. However, their widespread adoption depends on the availability of reliable and cost-effective charging systems.
Electric bus charging systems provide the power backbone that enables buses to operate smoothly throughout the day. These systems are designed to cater to different fleet sizes, operational hours, and route patterns. The most common charging methods include depot charging, opportunity charging, and inductive wireless charging.
Depot charging typically occurs overnight at bus terminals, allowing vehicles to recharge during non-operational hours. Opportunity charging, on the other hand, uses high-power chargers at bus stops or route terminals to quickly replenish energy during short breaks. Wireless or inductive charging systems, though still emerging, offer a contactless solution that improves convenience and reduces wear on charging connectors.
Each of these methods has its advantages depending on fleet operations and city infrastructure. As technology advances, many transport authorities are adopting hybrid approaches — combining depot and opportunity charging to optimize range, uptime, and operational efficiency.
Market Drivers Behind the Shift to Electric Bus Charging
Several key factors are propelling the global adoption of electric bus charging systems. The foremost driver is the increasing commitment of governments worldwide to reduce carbon emissions. With stricter environmental regulations and emission targets, cities are transitioning their public transport fleets to electric power.
Substantial investments in electric mobility infrastructure are also accelerating market growth. National and municipal governments are offering incentives, subsidies, and policy support for developing large-scale charging networks. This financial backing is encouraging public transit operators to upgrade from conventional fleets to battery-electric models.
Technological innovation is another major factor. Advances in battery capacity, charging speed, and power electronics have significantly reduced charging time and operational costs. Modern DC fast-charging systems can replenish an electric bus battery in under 30 minutes, allowing for continuous service without long downtimes.
In addition, the integration of smart grid technology enables charging systems to communicate with the energy network, balancing power demand and supply more efficiently. This helps avoid grid overload and allows operators to utilize renewable energy sources for cleaner, more sustainable charging.
Furthermore, as fuel prices fluctuate and maintenance costs for diesel buses rise, electric buses with efficient charging systems provide long-term economic benefits. Fleet operators can achieve significant savings in fuel, servicing, and operational expenses, making electrification a financially attractive choice.
Technological Innovations Powering the Industry
Electric bus charging systems are evolving rapidly with innovations that enhance performance, flexibility, and reliability. High-power DC charging solutions — capable of delivering up to 600 kW — are becoming the standard for rapid, opportunity-based charging. These systems reduce downtime and allow buses to maintain continuous routes throughout the day.
Pantograph charging, which connects automatically to the bus roof, is gaining traction in many urban networks. This hands-free system eliminates the need for manual plug-in connections, improving safety and efficiency. Similarly, modular charging hubs are being developed to serve multiple buses simultaneously, ensuring scalability for growing fleets.
Wireless or inductive charging represents the next frontier. Using electromagnetic fields, this technology allows buses to charge without direct contact, reducing wear and maintenance. It also enables in-motion charging, where vehicles recharge at designated points along their routes — a concept that could revolutionize future public transit systems.
Energy management software and telematics are further enhancing charging operations. AI-driven platforms analyze battery health, route data, and power demand to schedule optimal charging cycles, minimizing costs and extending battery life. Integration with renewable energy sources like solar and wind power adds another layer of sustainability.
Regional Insights and Market Outlook
North America and Europe currently lead the adoption of electric bus charging systems, supported by robust policy frameworks and sustainability goals. In Europe, nations such as the UK, Germany, and the Netherlands have made significant investments in zero-emission bus fleets and urban charging infrastructure.
Asia-Pacific, however, remains the fastest-growing region. China dominates the global electric bus market, accounting for the majority of the world’s fleet and charging infrastructure. Countries like India, Japan, and South Korea are also ramping up investments to modernize their public transport systems.
In Latin America and the Middle East, electric bus deployment is gaining momentum through international partnerships and renewable energy integration. As global awareness and government support continue to rise, more cities are expected to follow suit.
Conclusion
Electric bus charging systems are at the heart of sustainable urban mobility. By enabling faster, smarter, and more reliable recharging, they ensure that electric buses can operate efficiently and cost-effectively. With continuous technological innovation, government incentives, and the growing push for decarbonization, these systems are not just powering buses — they are powering the global transition to cleaner, greener, and smarter transportation networks.
Categorieën
Read More
Spiritual and Wellness Products Market 2025–2033: Industry Overview, Size, Trends, Key Segments & Top Companies The global Spiritual and Wellness Products Market is one of the fastest-growing niche segments in the broader health and wellness industry. As more people prioritize mental health, mindfulness, stress reduction, and holistic healing, demand for spiritual tools and...

Future of Executive Summary Hashimoto’s Disease Market: Size and Share Dynamics The global Hashimoto’s Disease Market was valued at USD 1.08 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 1.42 billion by 2032 During the forecast period of 2025 to 2032 the market is likely to grow at a CAGR of 3.50%, primarily driven by the rising prevalence of Hashimoto’s disease This...

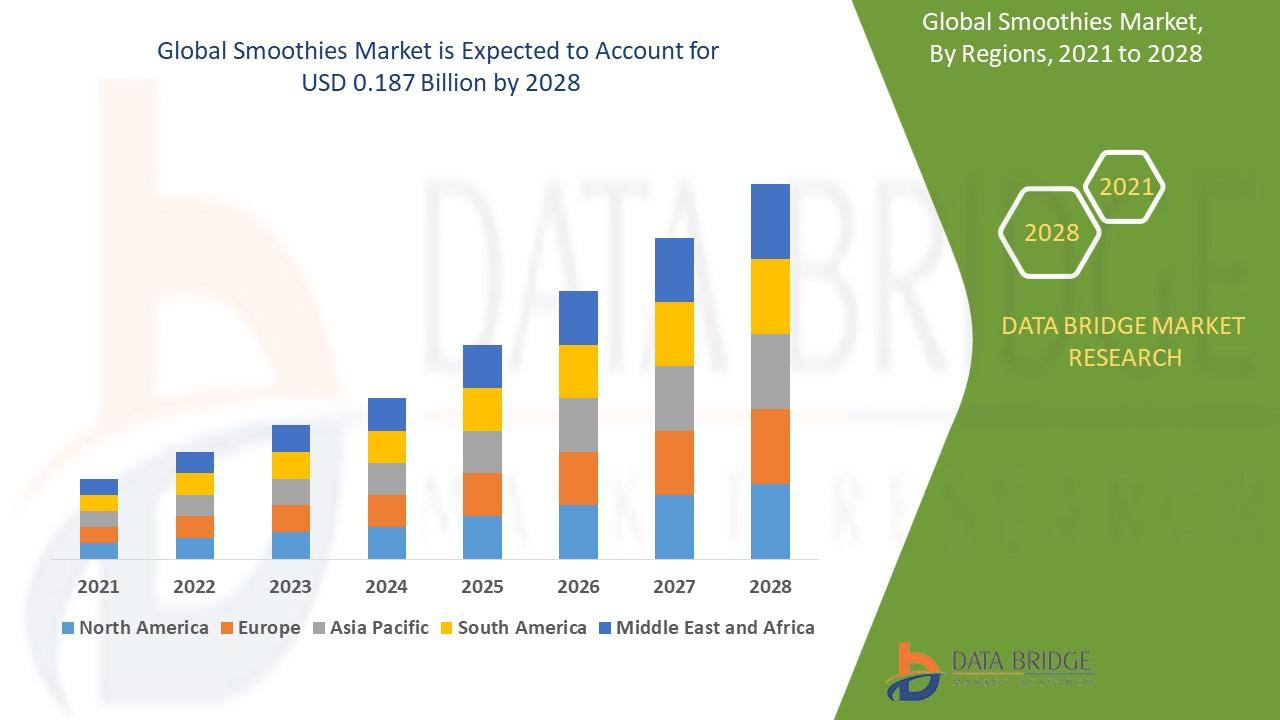
"Future of Executive Summary Smoothies Market: Size and Share Dynamics CAGR Value The global smoothies market size was valued at USD 127.72 million in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 273.78 million by 2032, with a CAGR of 10.00% during the forecast period of 2025 to 2032. The Smoothies Market report offers an analytical assessment of the prime challenges faced by the...
The latest business intelligence report released by Polaris Market Research on U.S. Beverage Packaging Equipment Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report By Automation (Manual, Semi-Automatic, Fully Automatic), By Application, By Type – Market Forecast, 2025–2034. It covers the in-depth knowledge of the U.S. Beverage Packaging Equipment Market Share that...

As per Market Research Future, the sodium ion battery market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for cost-effective and sustainable energy storage solutions. Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) have emerged as a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries due to the abundant availability of sodium, lower raw material costs, and comparable performance...
